Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, the choice of a database can significantly impact the performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of applications. With various data storage options available, ranging from traditional relational databases to modern NoSQL solutions, navigating through these choices can be daunting. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse range of database services offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS), detailing key characteristics, use cases, and potential limitations of each option.
Whether you’re building a small application or designing an enterprise-level system, understanding the distinct advantages of services like Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, and Amazon Redshift will help you make informed decisions. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of AWS databases and discover the right solution for your specific workload requirements.
1️⃣ Relational Databases (OLTP)
🔹 Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
Engines
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- MariaDB
- Oracle
- SQL Server
Key Characteristics
- Managed relational databases
- ACID compliant
- Automated backups, patching, Multi-AZ
- Vertical & limited horizontal scaling
Use Cases
- Traditional applications
- ERP / CRM systems
- Transactional workloads
- Applications requiring SQL joins and constraints
Limitations
- Scaling is slower
- Read replicas help reads, not writes
🔹 Amazon Aurora

Compatibility
- MySQL-compatible
- PostgreSQL-compatible
Key Characteristics
- Cloud-native distributed storage
- Up to 15 read replicas
- Faster failover than RDS
- Serverless option available
Use Cases
- High-performance OLTP
- SaaS platforms
- Mission-critical apps needing high availability
Why Aurora over RDS?
- Better performance
- Faster failover
- Higher scalability
2️⃣ NoSQL Databases (Key-Value / Document)
🔹 Amazon DynamoDB
Type
- Key-Value / Document NoSQL
Key Characteristics
- Fully serverless
- Single-digit millisecond latency
- Auto-scaling
- Global Tables

Use Cases
- Serverless applications
- IoT workloads
- Gaming leaderboards
- Session management
- Event-driven architectures
Common Pitfall
- Poor partition key design = throttling
🔹 Amazon Keyspaces (for Apache Cassandra)
Type
- Wide-column NoSQL
Key Characteristics
- Managed Cassandra
- No servers or patching
- Scales automatically
Use Cases
- Cassandra migrations
- Time-series data
- High-write workloads
3️⃣ In-Memory Databases & Caching
🔹 Amazon ElastiCache

Engines
- Redis
- Memcached
Key Characteristics
- Microsecond latency
- In-memory storage
- Reduces database load
Use Cases
- Read-heavy applications
- Session caching
- Leaderboards
- Real-time analytics
Redis vs Memcached
| Feature | Redis | Memcached |
|---|---|---|
| Persistence | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Replication | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Data types | Rich | Simple |
| HA | Yes | No |
🔹 Amazon MemoryDB for Redis

Type
- Durable in-memory database
Key Characteristics
- Redis-compatible
- Multi-AZ durability
- Transaction log persistence
Use Cases
- Financial services
- Real-time fraud detection
- Applications needing speed + durability
🔹 DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
Type
- In-memory cache for DynamoDB
Key Characteristics
- Fully managed
- Microsecond reads
- Write-through cache
Use Cases
- Read-heavy DynamoDB workloads
- Hot-key access patterns
4️⃣ Data Warehousing & Analytics (OLAP)
🔹 Amazon Redshift
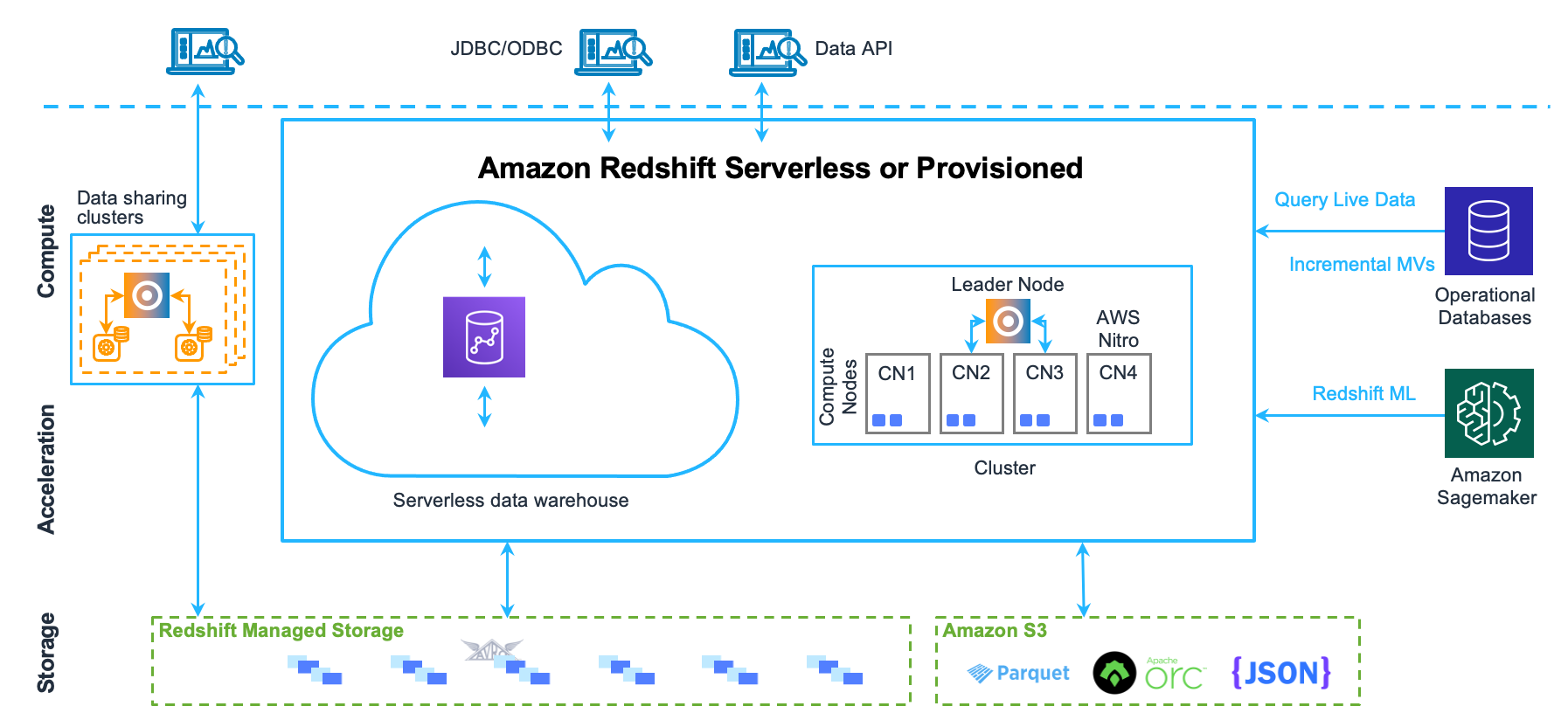
Type
- Columnar data warehouse
Key Characteristics
- Massively Parallel Processing (MPP)
- Optimized for analytics
- Integrates with S3 (Spectrum)

Use Cases
- Business intelligence
- Reporting
- Analytics dashboards
- Historical data analysis
Not For
- OLTP workloads
5️⃣ Search & Indexing
🔹 Amazon OpenSearch Service

Type
- Search & analytics engine
Key Characteristics
- Full-text search
- Log analytics
- Near real-time indexing
Use Cases
- Application search
- Log aggregation
- Security analytics (SIEM)
- Observability dashboards
6️⃣ Graph Databases
🔹 Amazon Neptune

Type
- Graph database
Key Characteristics
- Supports Gremlin & SPARQL
- Optimized for relationships
Use Cases
- Social networks
- Fraud detection
- Recommendation engines
- Network topology modeling

7️⃣ Ledger & Time-Series Databases
🔹 Amazon QLDB (Quantum Ledger Database)

Type
- Immutable ledger database
Key Characteristics
- Cryptographically verifiable
- Append-only
- No blockchain complexity
Use Cases
- Financial transactions
- Audit trails
- Compliance systems
🔹 Amazon Timestream

Type
- Time-series database
Key Characteristics
- Optimized for time-based data
- Automatic tiering
- SQL-like queries
Use Cases
- IoT telemetry
- Metrics & monitoring
- Application performance data
8️⃣ Document Database
🔹 Amazon DocumentDB (MongoDB Compatible)

Type
- JSON document database
Key Characteristics
- MongoDB API compatible
- Scales automatically
- Managed backups

Use Cases
- Content management
- User profiles
- JSON-heavy workloads
🧭 Decision Cheat Sheet
| Requirement | Service |
|---|---|
| ACID transactions | RDS / Aurora |
| Massive scale & low latency | DynamoDB |
| Caching | ElastiCache / DAX |
| Analytics | Redshift |
| Search | OpenSearch |
| Graph relationships | Neptune |
| Ledger | QLDB |
| Time-series | Timestream |
| Redis + durability | MemoryDB |
🚨 Common AWS Exam & Real-World Mistakes
- Using RDS for analytics instead of Redshift
- Forgetting ElastiCache is not durable (unless MemoryDB)
- Poor DynamoDB partition key design
- Using OpenSearch as a primary database
- Overusing Aurora when DynamoDB fits better
✅ Final Takeaway
AWS doesn’t have “one database.” It has the right database for each workload.
Understanding why each exists is the difference between clean architectures and expensive outages.



Leave a comment